The Complete Guide to Proxy Servers and Their Uses: An Ultimate Guide
A proxy server is a server that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or other resource available from a different server and the proxy server evaluates the request as a way to simplify and control its complexity.
Proxy servers are often used to increase security and privacy by protecting against unwanted traffic coming from malicious Internet users.
Proxy Servers Explained
A proxy server is a computer system that acts as an intermediary between the client and the Internet.
Proxy servers are commonly used to increase security and privacy, speed up browsing, and reduce bandwidth usage.
By visiting mywikistory and ecommerc you can get more knowledge about multiple topics.
A proxy server is a computer system that acts as an intermediary between the client and the internet. Proxy servers are often used to increase security, privacy, speed up browsing, and reduce bandwidth usage.
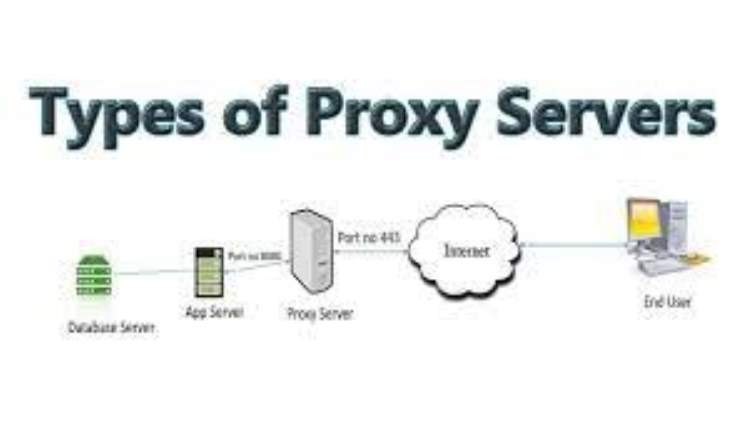
Types of Proxy Server
There are 2 types of proxy servers:
1. Transparent Proxy Server: The client computer doesn’t know that it is using a proxy server.
2. Non-transparent Proxy Server: The client computer knows that it is using a proxy server.
The common use cases for a transparent proxy server are to filter content, to provide anonymity, and to speed up internet browsing by caching content on the local machine.
The common use cases for a non-transparent proxy server are to access restricted websites and network resources, and to bypass firewalls or other network restrictions imposed by an organization or ISP.
The Importance and Benefits of Proxy Servers
A proxy server is a server that functions as an intermediary between an endpoint device and the Internet. It can be used to intercept and analyze all of the data that is being transmitted, while it also provides a degree of anonymity.
Anonymity is one of the most important benefits of using a proxy server. The connection between the endpoint device and the proxy server cannot be traced back to its original source. This means that it is much harder for anyone to identify who you are, what you are doing, or where you are located.
A proxy server can also help protect your privacy from other parties on your network; this includes ISPs, employers, schools, and even your own family members.
The Different Types of Proxies and How They Work
An HTTP proxy is a web-based proxy server that allows users to access the web anonymously. The user’s IP address is hidden from the website, and all requests from the user are redirected to a different computer.
An HTTP over HTTPS protocol is an extension of HTTP in which data transfer takes place through a secure channel that uses Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). It was designed to address some of the security concerns with unencrypted HTTP.
Proxies for anonymity, like those from proxy sale, purposes are servers that allow people to surf the internet without revealing their identity or IP address. They can be used for accessing blocked sites and services, bypassing censorship, and protecting privacy when using public networks.
Best Practices for Securing Your Proxy Server & Preventing Leaks from Occurring
A proxy server is a computer system that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or other resource available from a different server and the proxy server evaluates the request as a way to simplify and control its complexity. A proxy server has two connections: one connection is to the client asking for service; the other connection is to the remote server on behalf of whom it makes requests.
There are many potential threats that can lead to leakage of traffic on your network private cloud. Some of these are:
– Insecure data storage
– Incorrect configuration of access control lists
– Insufficient logging
– Insufficiently protected software updates
– Insufficiently protected network devices





